一、C#委托是什么?
1、在C#的委托之前,先了解一下C/C++的函数指针。
#include <stdio.h>
void (*funcP1)(void);
void PrintMessage()
{
printf("方法被调用\n");
}
void (*funcP2)(int, int);
void PrintSum(int a, int b)
{
printf("a+b=%d\n",a+b);
}
int main()
{
funcP1 = PrintMessage;
funcP2 = PrintSum;
funcP1();
funcP2(1,2);
PrintMessage();
PrintSum(1, 2);
}Out:
方法被调用
a+b=3
2、一切皆地址
变量是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值
函数是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令
① C/C++函数指针的汇编源码示例
从汇编代码来看C/C++函数指针的本质(内存中的一段机器指令):
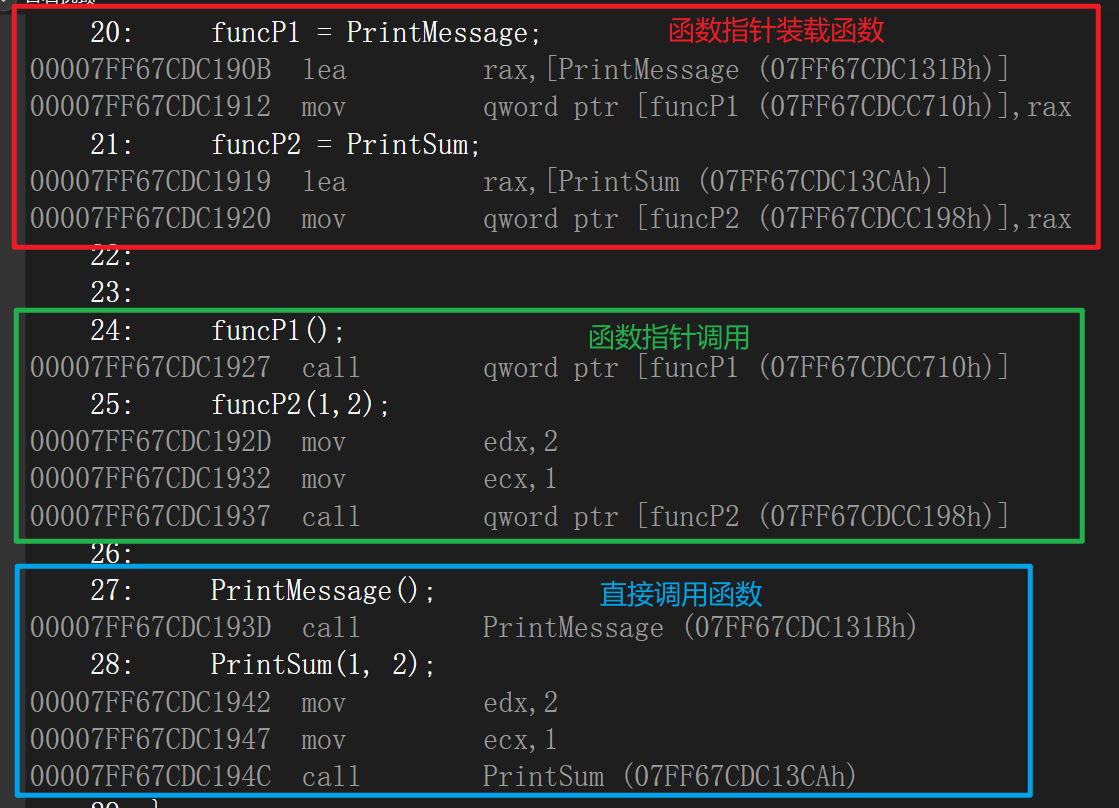
以funP1和PrintMessage为例讲解函数指针的汇编代码在内存层面都做了什么
20: funcP1 = PrintMessage;
00007FF67CDC190B lea rax,[PrintMessage (07FF67CDC131Bh)] //这行代码使用 lea 指令将 PrintMessage 函数的地址加载到寄存器 rax 中。
00007FF67CDC1912 mov qword ptr [funcP1 (07FF67CDCC710h)],rax //这行代码将 rax 中存储的 PrintMessage 函数的地址,存储到函数指针 funcP1 所指向的内存地址中。这样,funcP1 现在指向了 PrintMessage 函数。
24: funcP1();
00007FF67CDC1927 call qword ptr [funcP1 (07FF67CDCC710h)] //这行代码通过函数指针 funcP1 调用了 PrintMessage 函数。实际上,这行代码会跳转到 PrintMessage 函数的地址,然后执行 PrintMessage 函数中的代码。
27: PrintMessage();
00007FF67CDC193D call PrintMessage (07FF67CDC131Bh) //通过函数名直接调用函数则一样会跳转到 PrintMessage 函数的地址
综合起来,整个过程的目标是将函数指针 funcP1初始化为指向PrintMessage函数,并通过函数指针调用PrintMessage函数。
② C#委托类型的简单源码与汇编代码
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CalculateSum cal = GetIntSum;
cal.Invoke(1,2);
}
delegate void CalculateSum(int num1,int num2);
public static void GetIntSum(int num1, int num2)
{
Console.WriteLine(num1+num2);
}
}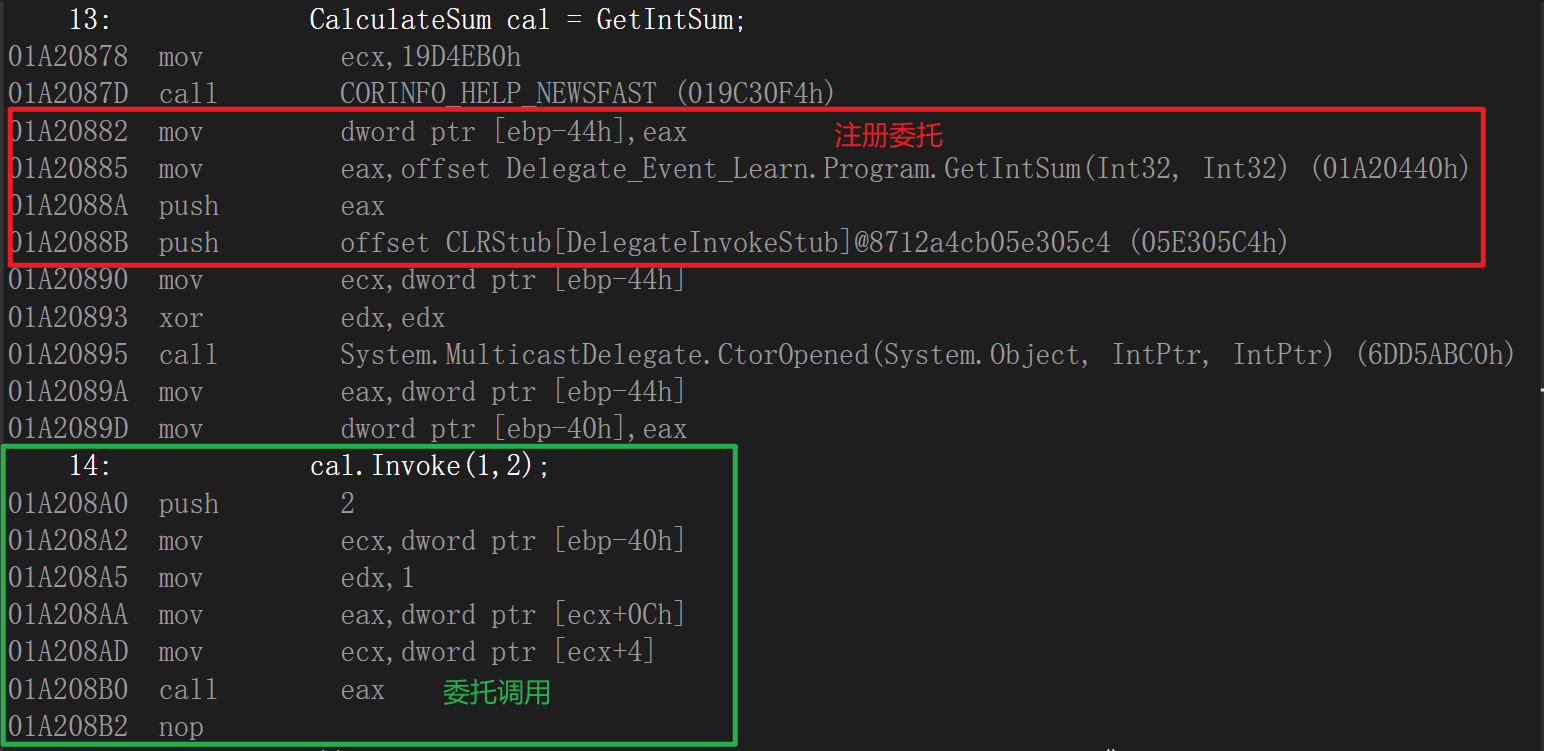
(因为C#的委托涉及到的知识较多,笔者修为还不够在此就不强行解释C#的汇编代码了)
③ C#委托的多播(多播委托)
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CalculateSum cal = Function1;
cal += Function2;
cal += Function3;
}
delegate void CalculateSum();
public static void Function1() { }
public static void Function2() { }
public static void Function3() { }
}C#委托与函数指针不同点之一就是:C#的委托可以注册多个方法,并且委托被调用时,函数按照注册顺序从前到后以此执行。
3、C#委托的简单总结
① 委托其实就是函数指针的“升级版”
从C/C++函数指针与C#委托的汇编源码对比来看,其实委托就是函数指针的“升级版”。
它们的核心逻辑就是记录函数方法的首地址,在委托调用时直接将执行位置跳转到该函数首地址。
② 委托的数据结构
如果你之前有了解过数据结构的链表,从多播委托不难看出委托的数据结构可以说是一根单链表,而每个节点都是注册的函数的首地址。
二、C#委托的使用
1、对委托的误解
肯定有不少C#初学者(包括我)在学到委托部分时,在看到示例代码时肯定一头雾水:“这跟直接调用函数有什么区别?”“搞这么麻烦,为什么不直接调用函数?”。
从汇编代码层面来看,委托确实起到了“函数的包装器”的作用,因为在调用委托和直接调用函数的时候,都是将执行位置跳转到函数的首地址。
但在经过一段时间项目(屎山)实战沉淀,我总结一句话:“存在即合理”。之所以会冒出“委托无用论”的想法,是因为接触的项目不够多以及项目体量不大,与委托有紧密联系的“事件”也是一样的(事件是委托的包装器),且这一块大多就已经涉及到设计模式相关知识了。
2、委托的广泛使用场景
C#委托常用于事件处理,回调函数,多播委托等,因为委托能将函数作为参数传递,从而提高了项目代码的灵活性和复用性。
3、委托的声明
① 自定义模版
delegate
return type:指定返回类型
delegate-name:该委托类的名称
parameter list:参数列表
delegate void CalculateSum<T>(T num1, T num2);
public static void Function1(int a, int b) { Console.WriteLine(a+b); }
static void Main()
{
CalculateSum<int> cal = Function1;
}
② 微软官方提供的委托模版,Action与Func
public delegate void Action<in T1, in T2>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2);Action返回值为void ,通过重载16次Action函数(最朴素的一集),允许最多16个形式参数。
微软官方文档链接:Action 委托 (System)
public delegate TResult Func<in T1, in T2, out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2);Func必须要有返回值,最后一个参数TResult为返回值类型,同样允许最多16个形参和1个返回类型
微软官方文档链接:Func
委托在注册方法实例时,方法和委托的参数列表之间的转换关系遵循C#的协变与逆变规则,详情请见微软文档:
协变和逆变 (C#)
in(泛型修饰符) - C# reference
out 关键字(泛型修饰符) - C# reference
引用类型支持泛型类型参数中的协变和逆变,但值类型不支持它们
简单的概况,在C#中,in和out关键字只可用于修饰接口或委托中的泛型类型参数(仅限引用类型)。in表示逆变性,允许使用更一般的(父类型)类型作为实参;out表示协变性,允许使用更特化的(子类型)类型作为实参。
在委托类型的声明中,通常对表示参数类型的泛型参数使用in修饰符,对表示返回值类型的泛型参数使用out修饰符。
PS:泛型类型参数均不使用in(Covariance)/out(Contravariance)关键字时,默认为“不变的”(invariant)。这也是为什么“in和out关键字只可用于修饰接口或委托中的泛型类型参数”,而泛型类的类型形参不能声明为协变或逆变;对于委托来说,invariant意味着方法的参数列表必须完全匹配委托实例的实参列表才可以进行注册。
4、委托的一般使用
将外部方法由委托包装后参数化,传给另一个方法内部来决定是否调用(间接的)。
① 正确使用1:模版方法,“借用”指定的外部方法来产生结果
·相当于选词(方法)填空
·常位于代码中部
·委托有返回值
利用委托类型能够在程序运行时动态的增删注册的函数,以此来提高代码的灵活性
using System;
namespace Delegate_Event_Learn
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WarpFactory warpFactory = new WarpFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePiza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCake);
Box box1 = warpFactory.WarpProductInBox(func1);
Box box2 = warpFactory.WarpProductInBox(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
public class Box : BigBox
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
public class BigBox
{ }
public class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePiza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Piza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeCake()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Cake";
return product;
}
}
public class WarpFactory
{
public Box WarpProductInBox(Func<Product> GetProduct)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = GetProduct.Invoke();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
}
② 正确使用2:回调方法(callback),调用制定的外部方法
·相当于“流水线”
·常位于代码末尾
·委托无返回值
using System;
namespace Delegate_Event_Learn
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WarpFactory warpFactory = new WarpFactory();
Func<Product> pizaProductionLine = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePiza);
Func<Product> cakeProductionLine = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCake);
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.LogProductionInfo);
Box box1 = warpFactory.WarpProductInBox(pizaProductionLine, log);
Box box2 = warpFactory.WarpProductInBox(cakeProductionLine, log);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
//回调方法
public class Logger
{
public void LogProductionInfo(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine($"产品{product.Name}于{DateTime.UtcNow}生产,价格是{product.Price}");
}
}
public class Box : BigBox
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
public class BigBox
{ }
public class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
}
public class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePiza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Piza";
product.Price = 20;
return product;
}
public Product MakeCake()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Cake";
product.Price = 10;
return product;
}
}
public class WarpFactory
{
public Box WarpProductInBox(Func<Product> GetProduct,Action<Product> logCallback)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = GetProduct.Invoke();
//根据价格判断是否执行回调方法
if(product.Price>15) logCallback.Invoke(product);
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
}
5、使用委托时需要注意的
委托是一种难精通、易使用、功能强大的东西、一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
·缺点1:委托是一种方法级别的“紧耦合”,实际项目中对委托的使用应该慎之又慎
·缺点2:使可读性降低,debug难度增加
·缺点3:将委托回调、异步调用、多线程纠缠在一起时,会让代码难以阅读和维护
·缺点4:委托使用不当有可能造成内存泄漏和降低程序性能。